Neurospine Hospital & Revive Critical Care
SEVERE INFECTIONS
Sepsis ( Severe Infections ) is a rare but serious complication of an infection. Without quick treatment, sepsis can lead to multiple organ failure and death.
Sepsis is the body’s extreme response to an infection. It is a life-threatening medical emergency. Sepsis happens when an infection you already have triggers a chain reaction throughout your body.
Infections that lead to sepsis most often start in the lung, urinary tract, skin, or gastrointestinal tract.
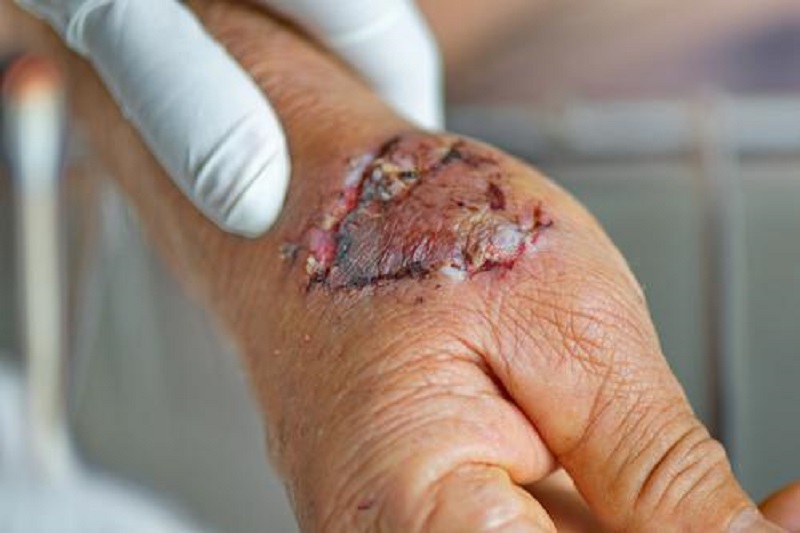
Symptoms of Severe Infections
- feeling dizzy or faint
- a change in mental state – like confusion or disorientation
- diarrhoea
- nausea and vomiting
- slurred speech
- severe muscle pain
- severe breathlessness
- less urine production than normal – for example, not urinating for a day
- cold, clammy and pale or mottled skin
- loss of consciousness
Treating Severe Infections
Treatment for sepsis varies, depending on the:
- area affected
- cause of the infection
- organs affected
- extent of any damage
If you have the early signs of sepsis, you’ll usually be referred to hospital. You’ll then be given a diagnosis and treatment.
Emergency Treatment
You’ll need emergency treatment, or treatment in an intensive care unit (ICU), if:
- the sepsis is severe
- you develop septic shock – when your blood pressure drops to a dangerously low level
ICUs can support body functions like breathing that are affected by sepsis. This allows the medical staff to focus on treating the infection.
Sepsis is treatable if it’s identified and treated quickly. In most cases it leads to full recovery with no lasting problems.
Risk Factor
- are very young
- are very old
- are pregnant
- have had a urinary catheter fitted
- have a long term health condition like diabetes
- have recently had surgery
- are genetically prone to infections
- are already in hospital with a serious illness
- have to stay in hospital for a long time
- have wounds or injuries as a result of an accident

