Hemodialysis Services In Nagpur
Hemodialysis
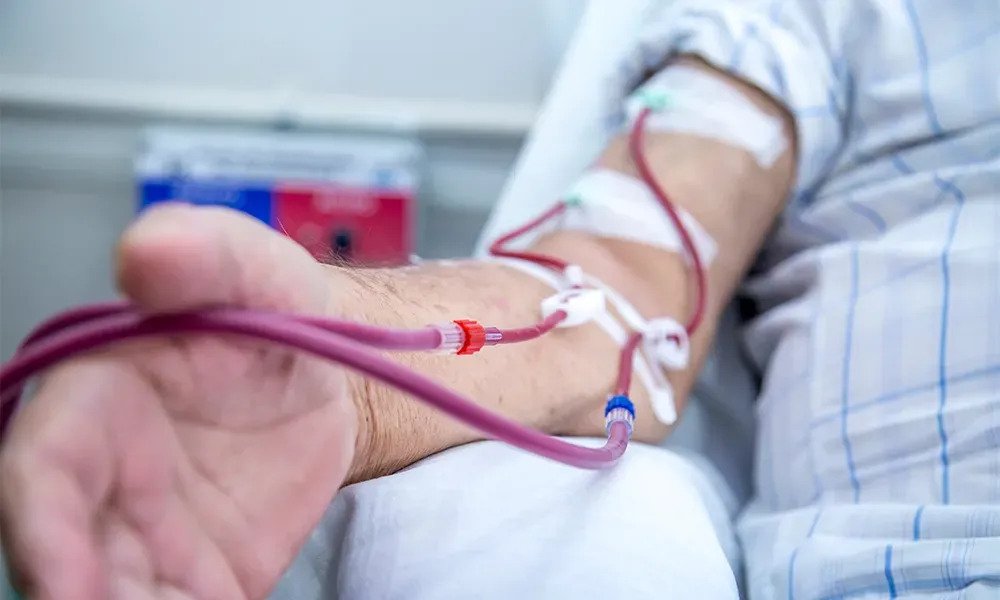
The process of hemodialysis involves several steps:
Vascular access: A vascular access site is created, usually by surgically joining an artery and a vein, or by using a catheter. This access point allows blood to be withdrawn from the body and returned after filtration.
Blood circulation: The patient’s blood is pumped from the access site into the dialysis machine, which contains the artificial kidney. The machine monitors and controls the flow rate of blood.
Filtration: Inside the dialysis machine, the patient’s blood flows through a series of tubes and filters. These filters selectively remove waste products and excess fluids from the blood, based on their size and charge.
Dialysate solution: At the same time, a dialysate solution, composed of water and electrolytes, flows in the opposite direction of the blood on the other side of the membrane.
Common Symptoms
Fatigue: Many people undergoing hemodialysis experience fatigue or a general feeling of tiredness. This can be due to the demands of the treatment process, changes in fluid and electrolyte balance, or the underlying kidney disease.
Low blood pressure: Hemodialysis can cause a drop in blood pressure, leading to symptoms such as dizziness, lightheadedness, or even fainting. Low blood pressure can occur during or after the dialysis session.
Muscle cramps: Some individuals may experience muscle cramps during hemodialysis, particularly in the lower limbs. These cramps can be caused by fluid and electrolyte imbalances, as well as the rapid removal of waste products during the procedure.
Nausea and vomiting: Hemodialysis can sometimes lead to nausea and vomiting, especially if there are rapid changes in fluid and electrolyte levels. These symptoms may also be related to the underlying kidney disease.
Itching: Many individuals undergoing hemodialysis experience itching, which is often due to the buildup of waste products and toxins in the blood. Dry skin and changes in mineral and vitamin levels can contribute to this symptom as well.
Treatment
Hemodialysis is a medical treatment used to filter and purify the blood when the kidneys are unable to perform their normal function of removing waste products and excess fluid from the body. It is primarily used to treat end-stage kidney disease or acute kidney injury.
During hemodialysis, blood is removed from the body through a surgically created access point, such as an arteriovenous fistula or graft, or through a catheter inserted into a large vein. The blood is then passed through a dialysis machine, which contains a special filter called a dialyzer or artificial kidney.
Inside the dialyzer, the blood flows through a series of hollow fibers that are surrounded by a dialysate solution. The dialysate contains electrolytes and other substances that help remove waste products from the blood. The waste products and excess fluid pass through the semi-permeable membrane of the fibers and are carried away by the dialysate, while the filtered blood is returned to the body.
Hemodialysis is typically performed in a specialized clinic, hospital, or dialysis center. The frequency and duration of hemodialysis sessions vary depending on the patient’s condition and the recommendation of their healthcare team. Generally, hemodialysis is performed three times a week, with each session lasting about 3 to 5 hours.
Precaution for Hemodialysis
Infection control: Hemodialysis patients are at a higher risk of infections. To prevent the spread of infection, healthcare providers and patients should follow strict hand hygiene practices. The dialysis equipment should be properly cleaned and disinfected, and sterile techniques should be used during catheter insertion or access site care.
Vascular access care: The access site, such as an arteriovenous (AV) fistula or graft, should be regularly monitored for signs of infection, clotting, or other complications. Proper care and hygiene of the access site can help prevent infections and maintain its patency.
Fluid and diet management: Hemodialysis patients have specific fluid and dietary restrictions. It’s important for patients to adhere to the prescribed fluid intake and follow a kidney-friendly diet. This helps maintain fluid balance and prevent electrolyte imbalances.
Medication management: Some medications may need to be adjusted for patients undergoing hemodialysis. It’s essential for patients to communicate their dialysis schedule to their healthcare providers so that medications can be appropriately timed and dosed.

